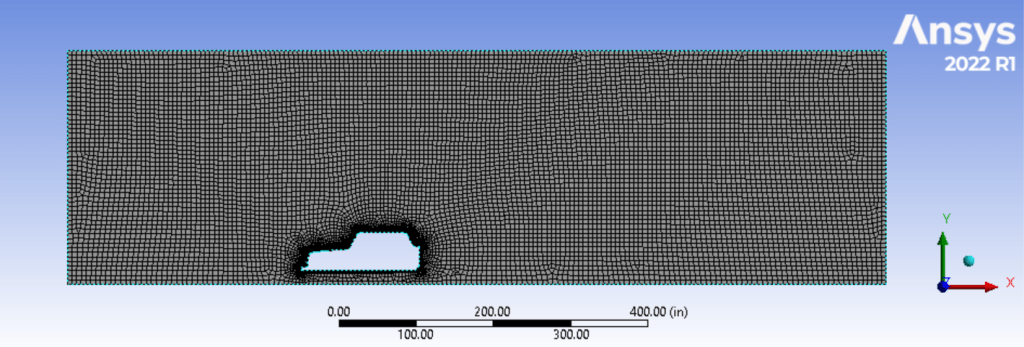
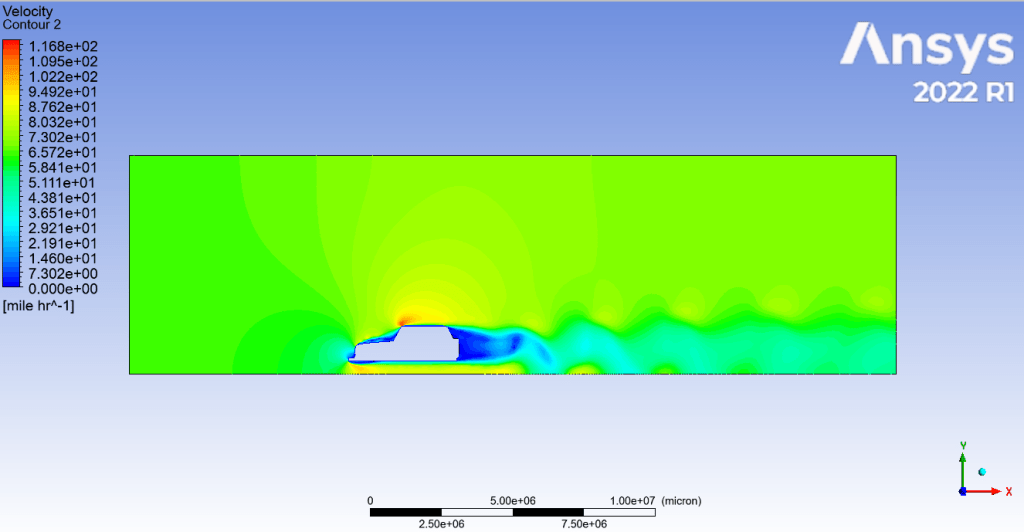
2D Fluent Flow Analysis Over Automobile
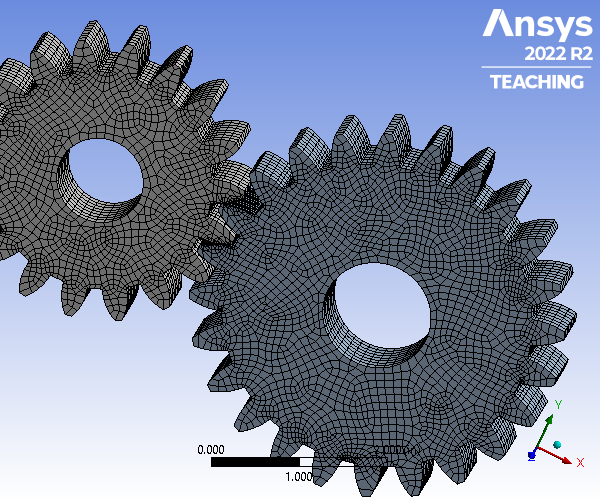
Static Structural Analysis of Spur Gears
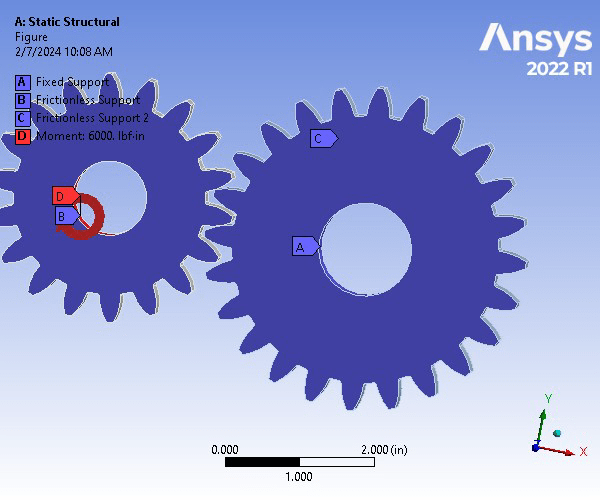
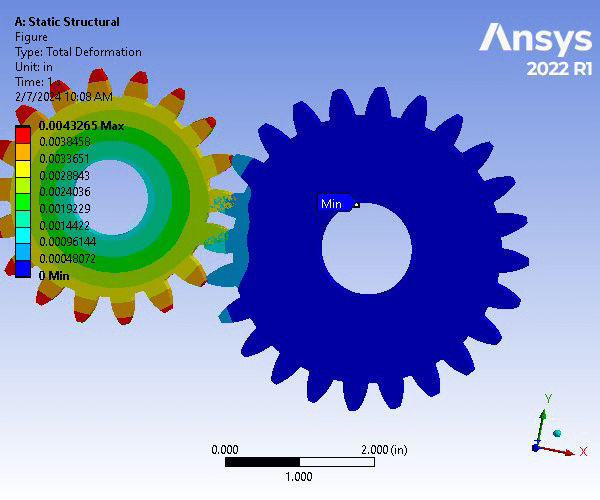
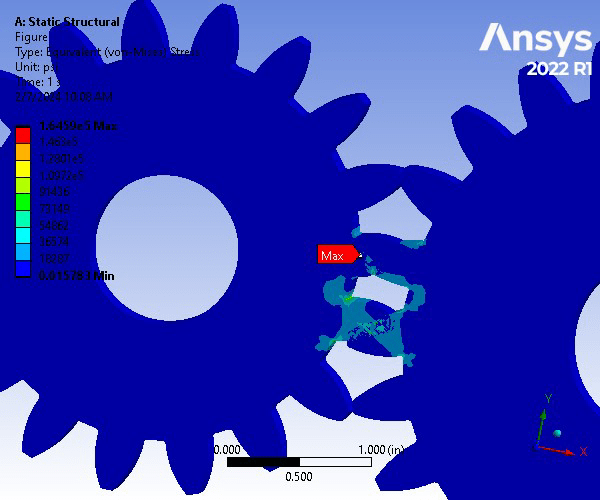
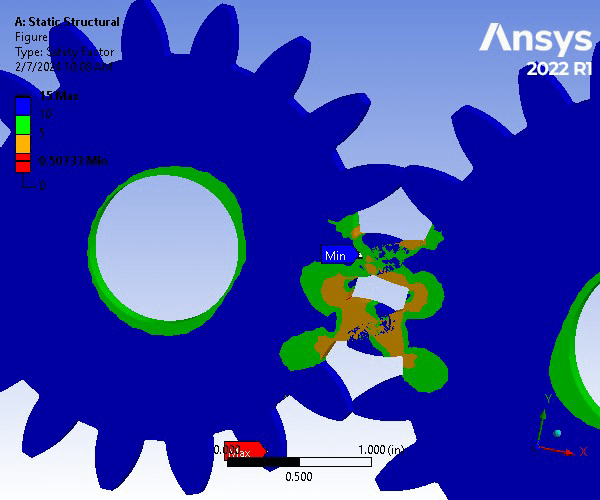
A gear set consisting of a pinion and spur gear is constructed of Structural Steel. The gear set underwent a Static Structural Analysis on ANSYS to determine the strength of the gear teeth. For an accurate analysis, the contact region between the two was set to be frictionless to allow for the movement and meshing between the gear teeth. The two bodies were assigned a 0.1 in mesh size. To focus on the where the teeth will be meshing, an edge size refinement was assigned that created 40 divisions along the specified edges. Next, the spur gear was assigned a fixed support on the inner face of the gear, whereas the pinion gear was assigned a frictionless support on its inner face. Next, a frictionless support was assigned to the front and back faces of both gears. Finally, a moment of -6000 lbf was applied in the z-direction of the inner surfaces of the pinion gear. The resulting factor of safety for a million cycles was 0.507 and is therefore an unsafe design.
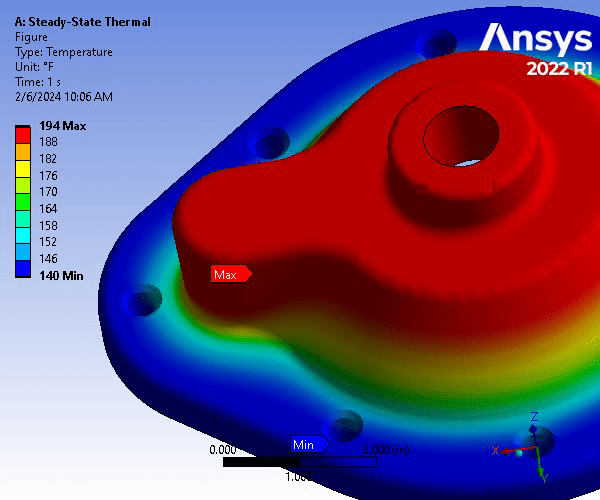
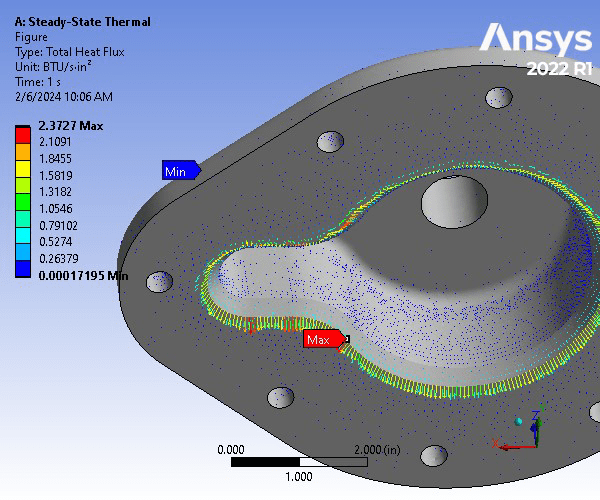
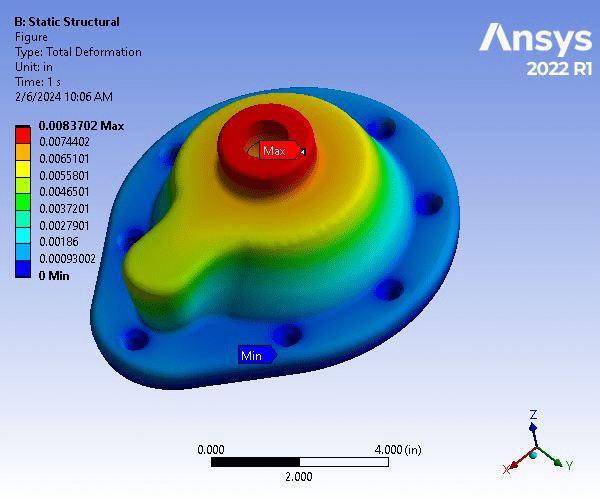
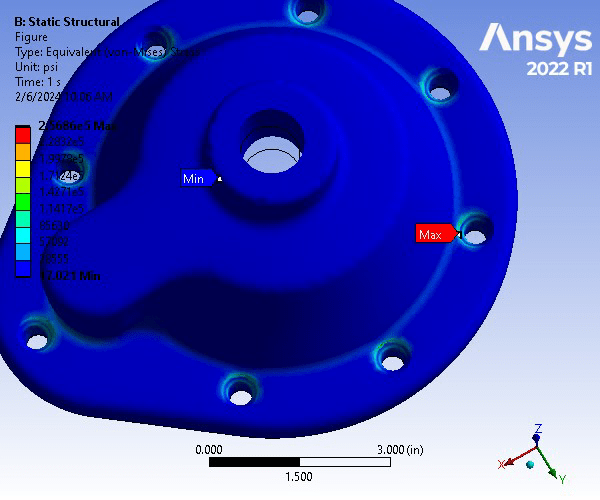
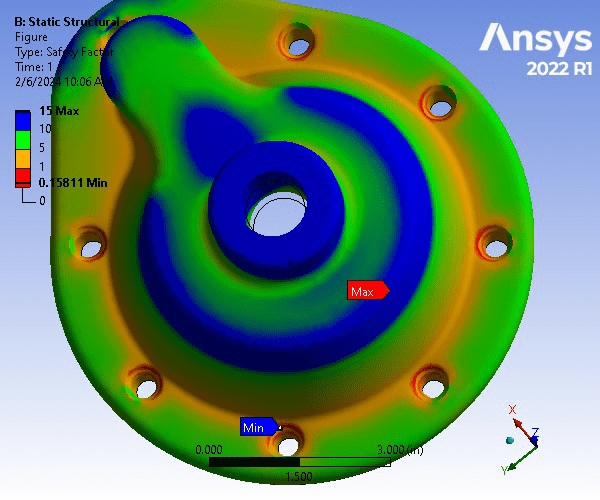
Static Structural Analysis of Pump Housing Cover
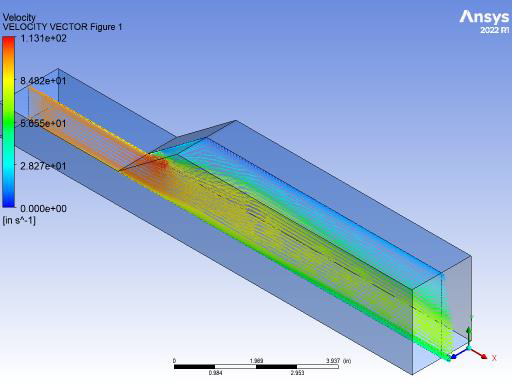
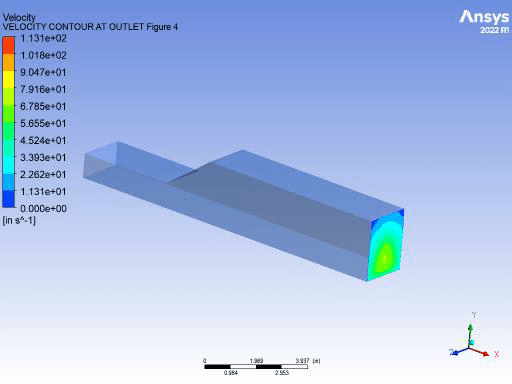
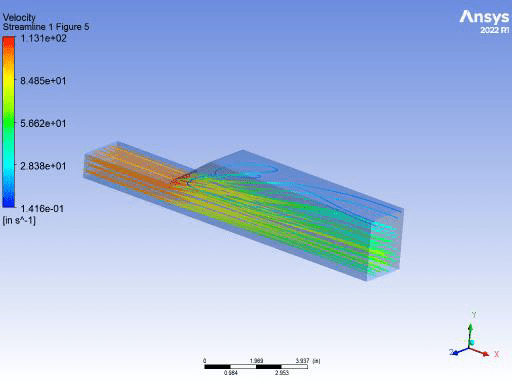
Fluent Flow Analysis of Flow Through 3D Duct
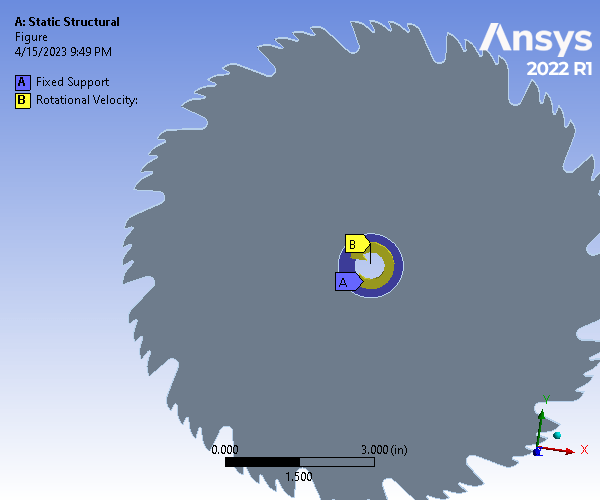
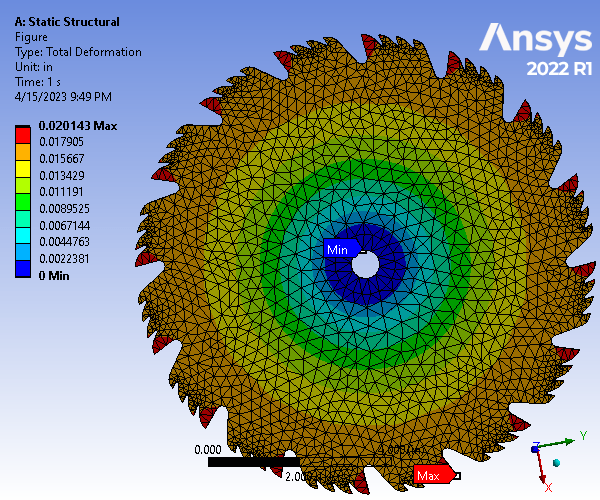
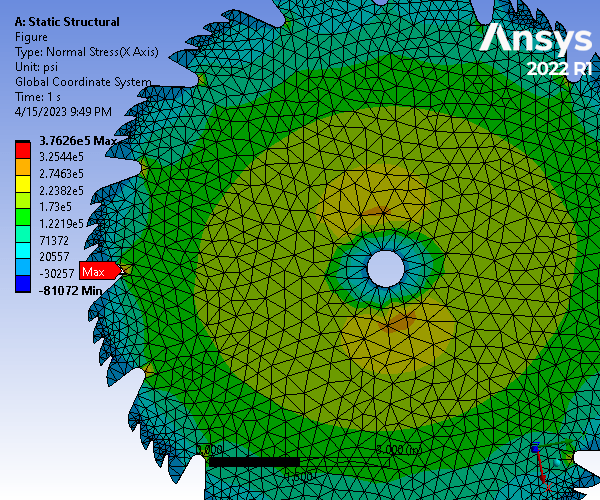
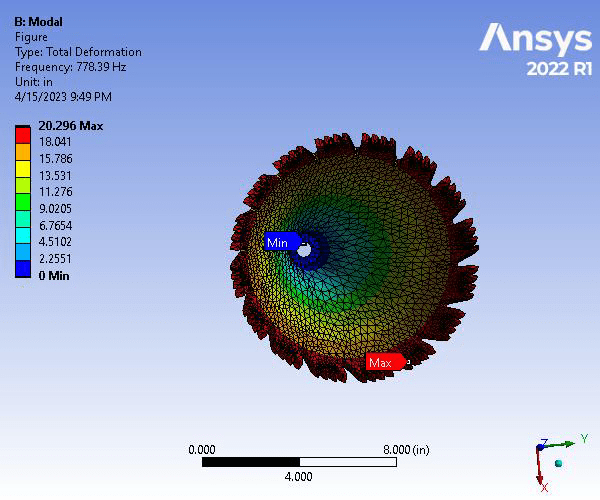
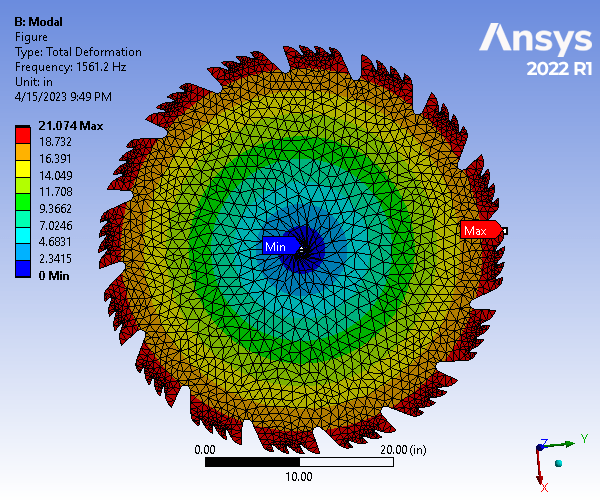
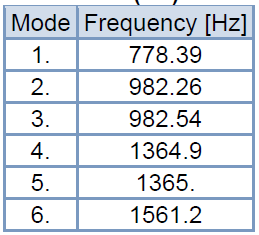
Static Structural and Modal Analysis of Rotating Saw Blade
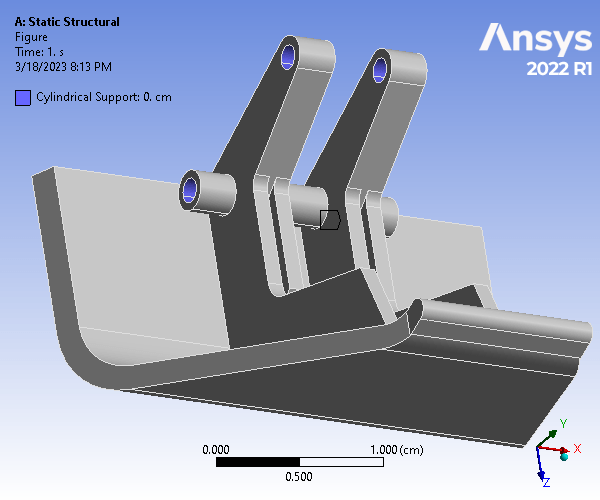
Static Structural and Modal Analysis of a Hood Latch
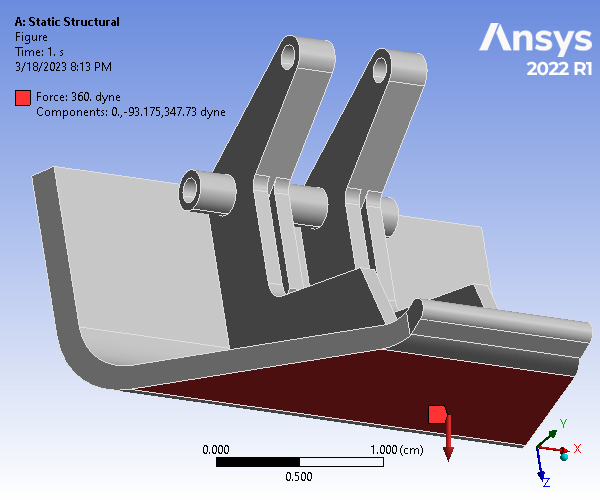
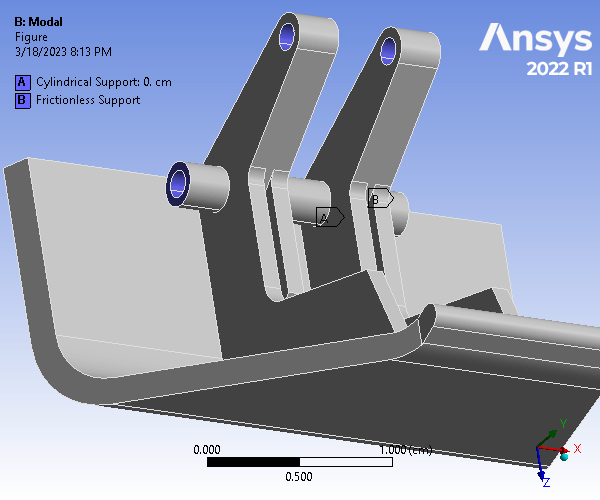
The given hood latch was modeled on Creo and simulated using ANSYS Static Structural and Modal analyses. The part was analyzed using a 0.04cm mesh size, and a mesh refinement was applied to 6 rounded surfaces. To constrain the model, cylindrical supports were assigned to all cylindrical surfaces, and a fixed support was applied to the two outer surfaces of the bottom cylindrical hole. Finally, a 360 dyne force loading was applied to the large outer surface, normal to and coming out of the geometry. For the analysis, Weak Springs (program controlled) were utilized.
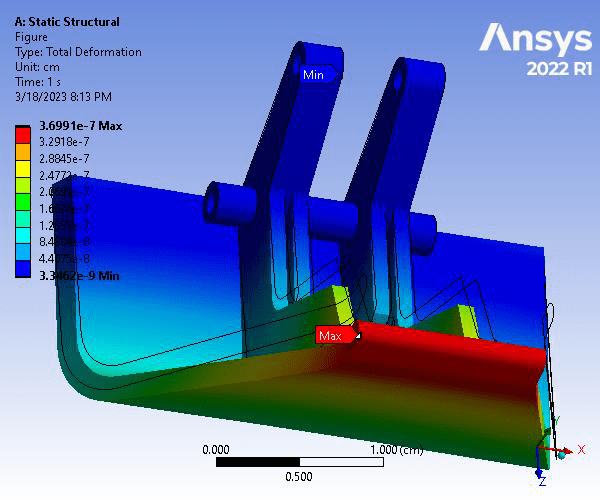
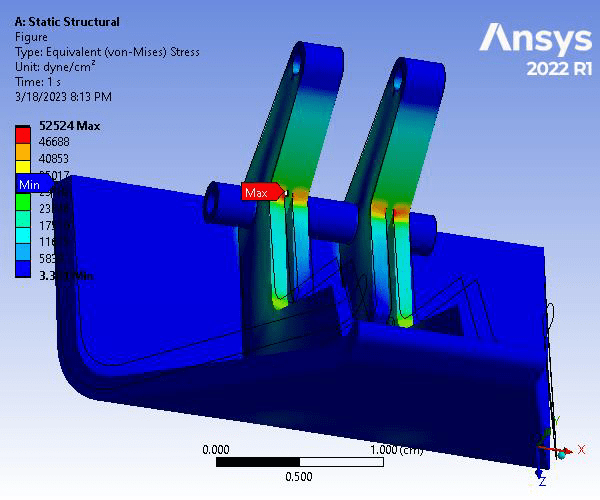
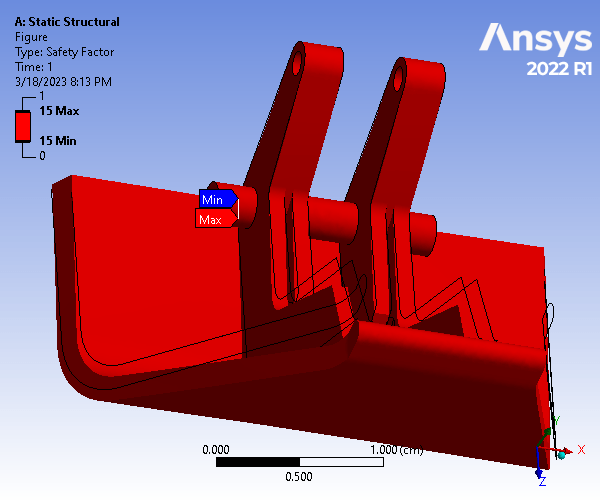
The resulting Total Deformation, Equivalent (von Mises) Stress, Convergence Factor, and Factor of Safety were found. The maximum deformation of the part occurred on the top portion of the hood latch, with a magnitude of 3.6991e-007 cm. The maximum von Mises stress occurred at rounded surfaces shown, with a magnitude of 52524 dyne/cm^2. The convergence factor was about 1.8684%. Finally, the resulting FS of the model under the given loading and constraints was determined to be 15 which is more than adequate.
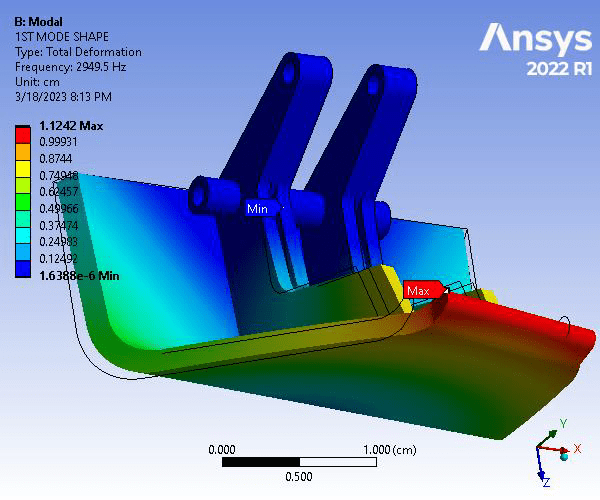
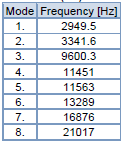
Due to the nature of the part’s usage and loading, a modal analysis. A total of 8 modes were simulated. At the 8th mode (21017 Hz), the part underwent significant deformations than can be observed from both the provided figure as well as the simulated animation. It is obvious that the deformations resulting from the differing frequencies, under the same constraints as the static structural analysis, were more severe than that shown in the total deformation plot. Hence, it is important to analyze parts like this both by static structural and modal analyses.